What is Major Autohemotherapy (MAH)?
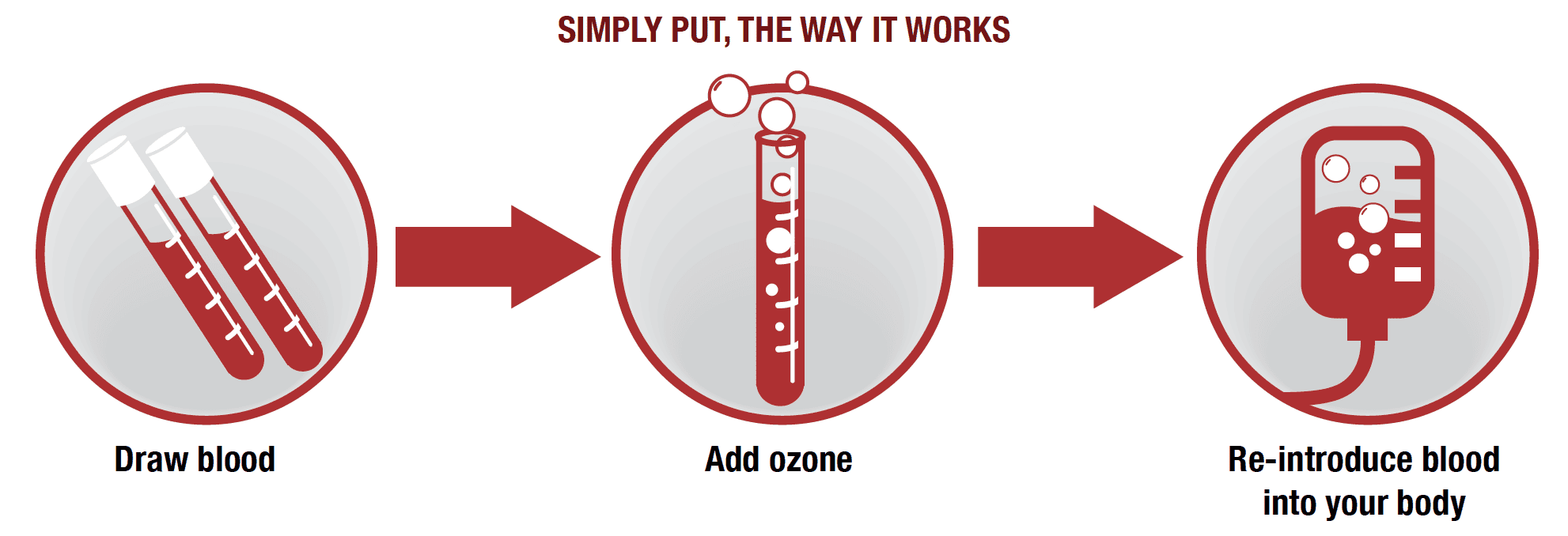
Autohemotherapy is a medical treatment that involves withdrawing a patient's blood, modifying it with ozone or other substances, and reintroducing it into the patient's bloodstream. This therapy is divided into two main types: major autohemotherapy (MAH) and minor autohemotherapy.
MAH involves withdrawing a larger amount of blood and adding ozone to it, while minor autohemotherapy involves injecting a small amount of ozone directly into the patient's bloodstream.
Autohemotherapy has become increasingly popular as a complementary treatment for cancer patients. It can help improve the overall health of the patient, boost the immune system, and increase the effectiveness of other treatments. In this article, we will explore the different types of autohemotherapy, their benefits, and their potential risks.
How Does Major Autohemotherapy (MAH) Work?
Major autohemotherapy (MAH) involves withdrawing more blood from the patient, typically between 100 and 300 ml, and mixing it with ozone. The ozonated blood is then reintroduced back into the patient's bloodstream via an IV drip. The ozone added to the blood helps to stimulate the immune system, increases oxygenation of the body's tissues, and promotes healing.
MAH has been used to treat a wide range of medical conditions, including cancer, viral infections, chronic fatigue syndrome, and autoimmune disorders. Many cancer patients find that MAH improves their quality of life, reduces the side effects of chemotherapy and radiation, and helps to prevent cancer recurrence.
What are the Benefits of Autohemotherapy?
Autohemotherapy has several potential benefits for cancer patients. It can:
- Improve overall health: Autohemotherapy can help to boost the immune system, reduce inflammation, and promote the body's natural healing processes.
- Increase oxygenation: Ozone added to the blood can help increase oxygenation of the body's tissues, improving energy levels and overall well-being.
- Reduce side effects of chemotherapy and radiation: Many cancer patients experience side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and fatigue during chemotherapy and radiation. Autohemotherapy can help to reduce these side effects and improve quality of life.
- Improve the effectiveness of other treatments: By boosting the immune system and promoting healing, autohemotherapy can help to improve the effectiveness of other cancer treatments.
How Can Ozone Autohemotherapy Treatment Help Cancer Patients?
Ozone autohemotherapy can help cancer patients in several ways. First, it can stimulate the immune system, often suppressed in cancer patients. By boosting the immune system, ozone autohemotherapy can help to improve the body's ability to fight cancer cells.
Second, ozone autohemotherapy can help to reduce inflammation, which is often a key factor in the development and progression of cancer. By reducing inflammation, ozone autohemotherapy can help slow cancer cell growth and spread.
Finally, ozone autohemotherapy can help to increase oxygenation of the body's tissues, which is essential for healing and recovery. By increasing oxygenation, ozone autohemotherapy can help to improve energy levels and overall well-being.
What Conditions Can Benefit from Major Autohemotherapy?
Major autohemotherapy has been used to treat a wide range of medical conditions, including:
- Cancer
- Viral infections
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
- Autoimmune disorders
- Chronic pain
- Allergies
- Asthma
- Arthritis
In cancer patients, MAH can help to improve overall health, reduce the side effects of chemotherapy and radiation, and increase the effectiveness of other cancer treatments.

What is the Process for Major Ozone Autohemotherapy Treatment?
Major ozone autohemotherapy (MAH) is a type of ozone therapy that involves the administration of ozone into the bloodstream through autohemotherapy, which is the withdrawal of a patient's blood, exposure to ozone, and reinfusion into the body.
During the MAH process, a small amount of blood is withdrawn from the patient and mixed with a medical-grade ozone-oxygen mixture. The mixture is then reinfused into the patient's body.
The amount of ozone used in the mixture can vary depending on the patient's condition but generally ranges from 10 to 60 µg/mL. The treatment can last anywhere from 10 minutes to an hour, and the frequency and duration of treatment sessions depend on the individual patient's needs.
What is the Difference Between Major Autohemotherapy (MAH) and Ozone High-Dose Therapy (OHT)?
While both MAH and ozone high-dose therapy (OHT) involves the administration of ozone into the bloodstream through autohemotherapy, there are some key differences between the two treatments.
MAH involves the use of a lower concentration of ozone (between 10 to 60 µg/mL) and is typically performed more frequently (two to three times per week) over a longer period of time (several months). OHT, on the other hand, involves the use of a higher concentration of ozone (up to 70 µg/mL) and is typically performed less frequently (once or twice per week) over a shorter period of time (a few weeks to a few months).
What is the Difference Between Minor Autohemotherapy and Major Autohemotherapy?
Autohemotherapy is a treatment where a patient's blood is withdrawn and re-injected to address various health conditions. There are two types of autohemotherapy: minor and major. The difference between the two is the amount of blood withdrawn and re-injected.
Minor autohemotherapy involves withdrawing a small amount of blood, typically around 10 milliliters, from the patient and then injecting it back into the patient's muscle tissue. This stimulates the immune system and is often used to treat allergies, infections, and autoimmune diseases.
On the other hand, major autohemotherapy involves withdrawing much more blood, often around 200 milliliters, and mixing it with an ozone-oxygen mixture before re-injecting it into the patient's bloodstream. This process stimulates the immune system more profoundly and is used to treat more severe health conditions, including cancer.
The major difference between minor and major autohemotherapy is the amount of blood that is withdrawn and the way in which it is re-injected. While minor autohemotherapy is generally considered safe and is associated with minimal risks, major autohemotherapy carries a slightly higher risk due to the larger amount of blood being withdrawn and re-injected.
What are the Risks of Major Autohemotherapy?
While major autohemotherapy has been shown to be an effective treatment for a variety of health conditions, such as Cancer at Brio-Medical, there are some risks associated with the procedure. The most common risks include:
- Infection: Anytime the skin is penetrated, there is a risk of infection. This risk is minimized by using sterile techniques and equipment during the procedure.
- Bleeding: Withdrawing a large amount of blood can increase the risk of bleeding. Patients who are taking blood-thinning medications or who have a bleeding disorder may not be good candidates for major autohemotherapy.
- Allergic reaction: Some patients may be allergic to the ozone-oxygen mixture used in major autohemotherapy. This risk can be minimized by performing a small skin test prior to the procedure.
- Fatigue: After major autohemotherapy, some patients may experience fatigue or weakness. This is a normal side effect and typically resolves within a few days.
Like any medical procedure, there are potential risks associated with major autohemotherapy (MAH). However, the risks associated with MAH are generally low and are typically outweighed by the potential benefits.
Who Can Not Receive Ozone Autohemotherapy Treatment?
While ozone autohemotherapy has been shown to be an effective treatment for various health conditions, certain groups of people may not be good candidates for the procedure. These include:
- Pregnant women: The effects of ozone on developing fetuses are not well understood, so it is recommended that pregnant women avoid ozone therapy.
Pregnancy is a delicate state that requires caution regarding any form of treatment. Autohemotherapy, which involves the withdrawal and re-injection of blood, may pose some risks to pregnant women. This is because, during pregnancy, the body undergoes numerous changes that can affect the body's ability to handle certain treatments.
Autohemotherapy may lead to anemia in pregnant women, a condition in which the body doesn't have enough red blood cells to carry oxygen to the body's tissues. This can be dangerous to both the mother and the baby, as it can lead to complications such as preterm labor, low birth weight, and developmental problems in the baby. Additionally, the use of heparin during autohemotherapy can pose a risk to pregnant women, as heparin can increase the risk of bleeding and other complications during pregnancy.
- GD6P Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase) Deficiency:
GD6P deficiency is a genetic disorder that affects the body's ability to produce a specific enzyme, which can lead to a buildup of certain types of sugars in the body's cells. Autohemotherapy may not be suitable for individuals with GD6P deficiency, as the use of heparin during treatment may pose a risk to these individuals. Heparin has been shown to inhibit the function of the enzyme affected by GD6P deficiency, which can lead to a further buildup of sugars in the body's cells.
Furthermore, individuals with GD6P deficiency may be at an increased risk of developing anemia during autohemotherapy. This is because the condition can affect the production of red blood cells in the body, which can lead to a decreased ability to carry oxygen to the body's tissues. Individuals with GD6P deficiency should consult with their healthcare provider before considering autohemotherapy as a form of treatment.
- People with hyperthyroidism: Ozone therapy has been shown to stimulate the thyroid gland, which can exacerbate symptoms in people with hyperthyroidism.
Hypothyroidism is when the thyroid gland doesn't produce enough thyroid hormone. This can lead to many symptoms, such as fatigue, weight gain, constipation, and depression. Autohemotherapy is a form of treatment involving the withdrawal of blood from a patient and re-injection into the patient's body. While autohemotherapy is generally considered safe, individuals with hypothyroidism should be cautious when considering this therapy.
The thyroid gland plays a vital role in regulating the body's metabolism, which is the rate at which the body burns calories to produce energy. Hypothyroidism can lead to a slowdown in the metabolism, causing individuals to gain weight and feel fatigued. The use of autohemotherapy in individuals with hypothyroidism may lead to an increased demand for thyroid hormones, which can exacerbate the symptoms of hypothyroidism.
-
Active Bleeding or Acute Hemorrhagic Disease (i.e., Hemophilia): People with active bleeding or acute hemorrhagic disease, such as hemophilia, have a higher risk of bleeding complications. Hemophilia is a genetic disorder that impairs the body's ability to control blood clotting. In these individuals, the blood takes longer to clot, leading to excessive bleeding or even internal bleeding. The procedure can aggravate their condition, leading to life-threatening complications.
-
Acute MI (acute myocardial infarction): Also known as a heart attack, Acute MI is a medical emergency caused by obstructing the blood supply to the heart muscle. This condition requires immediate medical intervention, and autohemotherapy may interfere with the standard treatment procedures. The procedure can also pose a risk of further heart damage, leading to more severe complications.
-
Allergy to Heparin: Heparin is a blood-thinning medication that can prevent blood clots from forming or growing larger in the body. Some people may develop an allergy to heparin, leading to serious allergic reactions. Autohemotherapy involves the use of heparin in the process. People with a known allergy to heparin should not undergo this treatment as it can trigger an allergic reaction that can be life-threatening. It is important to identify potential allergies before any procedure that involves heparin to prevent severe reactions.


